Education
Sub Category
A unit is a frequently arbitrary designation we have given to something to convey a definite magnitude of a physical quantity and every quantity can be expressed in terms of the seven base units that are contained in the international system of units. Hank thinks this is a thrilling subject, and while you may not agree, it is a subject that is very important if you want to be a scientist and communicate with accuracy and precision with other scientists. So listen up and learn something or Hank might have to kill you! (NOT REALLY!)
Watch this video in Spanish on our new Crash Course en Español channel! https://youtu.be/aMrxhohbkVA
Pssst... we made flashcards to help you review the content in this episode! Find them on the free Crash Course App!
Download it here for Apple Devices: https://apple.co/3d4eyZo
Download it here for Android Devices: https://bit.ly/2SrDulJ
Table of Contents
Unit Conversion 02:27
Scientific Notation 03:26
Sig Figs 07:40
Crash Course is on Patreon! You can support us directly by signing up at http://www.patreon.com/crashcourse
Want to find Crash Course elsewhere on the internet?
Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse
Twitter - http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/thecrashcourse/
CC Kids: http://www.youtube.com/crashcoursekids
View full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/the-....genius-of-mendeleev-
The elements had been listed and carefully arranged before Dmitri Mendeleev. They had even been organized by similar properties before. So why is Mendeelev's periodic table the one that has endured? Lou Serico explains via eka-aluminum, an element whose existence Mendeelev predicted years before it was discovered.
Lesson by Lou Serico, animation by TED-Ed.
This is a chemistry 101 video on atoms: What are atoms? The world is made of 92 different kinds of atoms.
Subscribe to watch more online chemistry courses & science videos:
http://www.youtube.com/channel..../UCiX8pAYWBppIbtUZTf
About Atomic School:
Atomic School supports the teaching of Atomic Theory to primary school & science students .
We provide lesson plans, hands-on classroom resources, demonstration equipment, quizzes and a Teacher's Manual to primary school teachers. Animated videos that clearly explain the scientific ideas supports learning by both teachers and students. As a teacher, you don't have to look anywhere else to implement this program.
Our work has been verified by science education researchers at the University of Southern Queensland, Dr Jenny Donovan and Dr Carole Haeusler, who confirm that primary students are capable of learning much more complex scientific concepts than previously thought, and crucially, that they love it. Students run to class!
The program has been trialed in Australian schools as well as high schools in the Philippines, Iran and India. It is conducted as holiday workshops at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation, the Queensland Museum as well as the World Science Festival.
It has attracted wide media interest, including TV, radio and print, and the research data has been presented at prestigious American Education Research Association and Australian Science Education Research Association conferences.
Atomic Theory underlies all the other sciences- genetics, electronics, nanotechnology, engineering and astronomy- so an early understanding will set them up for a more successful learning sequence for all their science subjects, and support their mastery of mathematics as well. We also have extension programs that cover Biology, Physics and Astronomy to an equal depth.
About Ian Stuart (Email: ian.douglas.stuart@gmail.com):
The founder of Atomic School, Ian Stuart, taught Chemistry and Physics for 25 years at senior levels before he realized that his 8-year old son, Tom, could understand Atomic Theory at a much deeper level than he expected. After visiting Tom's class at school, he discovered that his peers could also grasp the abstract scientific concepts, as well as apply it usefully to the real world.
Ian then developed a program to teach the advanced concepts of high school Chemistry, Physics and Biology to students 10 years younger than they normally would. He found that this engaged their interest in modern science early, and sustained it through to high school and beyond. It also sets them up for future success in their academic and career paths.
Ian has a Bachelor's Degree in Chemistry from the University of Queensland and a Master's degree in Electrochemistry from the University of Melbourne.
Connect with Atomic School on social media:
http://facebook.com/AtomicSchool
http://twitter.com/AtomicSchools
http://instagram.com/AtomicSchools
Video transcript:
From a distance, a beach looks like one big smooth thing. But if we look at it through a telescope, we can magnify it and make it look bigger. Now we can see that the beach is not smooth at all, and it's not a single thing. It's made up of a lot of little sand grains. The beach is nothing but all the little sand grains put together. 12. A beach can be made of a thousand TRILLION sand grains.
It's an example of a big thing being made of lots of little things. We could say that the sand grains are the basic building blocks of the beach. How about a forest made of lots of trees? Here's a forest up close, and here's a forest on a distant mountain. Is this Lego parrot just one thing?
We can say that bricks are the basic building blocks of the hut, or that sand grains are the basic building blocks of the beach. But are bricks or sand grains themselves made of anything smaller?
To answer this question we can magnify a sand grain to see what it's made of. Scientists magnify really small things using a microscope, which will make the sand grain look bigger. The most powerful kind is called an electron microscope which can make things look millions of times bigger, so let's use that. Our scientist puts some sand under the microscope and now she looks through the top to see the magnified sand. Here's what she sees when she zooms in. This is what she sees, and now she is zooming in more. Magnifying the sand grain a million times would let her see the sand's building blocks.
Wow, look at those. These marble-shaped particles are the building blocks of the sand. They're called atoms. The word atom means uncuttable, and if you imagine we had a very sharp knife, we could cut the sand into smaller and smaller pieces, but we couldn't make it smaller than an atom because this is the sand's smallest piece. A tiny sand grain is made of 10 million, TRILLION atoms
This video provides a basic introduction for college students who are about to take the 1st semester of organic chemistry. It covers topics such as polar and nonpolar bonds, ionic & covalent bonding, alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, bond length, bond strength, sigma & pi bonds, hybridization, formal charge, functional groups and drawing lewis structures.
Access The Full 1 Hour 42 Minute Video:
https://www.patreon.com/MathScienceTutor
Direct Link to The Full Video on Patreon:
https://bit.ly/3k8oRUW
Organic Chemistry PDF Worksheets:
https://www.video-tutor.net/orgo-chem.html
_______________________________________
Full 1 Hour 42 Minute Video on YouTube:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jxvU_GH3mWo
IUPAC Nomenclature:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TYU_JluleME
Join The YouTube Membership Program:
https://bit.ly/46xaQTR
Hank gives us a tour of the most important table ever, including the life story of the obsessive man who championed it, Dmitri Mendeleev. The periodic table of elements is a concise, information-dense catalog of all of the different sorts of atoms in the universe, and it has a wealth of information to tell us if we can learn to read it.
Watch this video in Spanish on our Crash Course en Español channel! https://youtu.be/AmOl0v_3jsc
Pssst... we made flashcards to help you review the content in this episode! Find them on the free Crash Course App!
Download it here for Apple Devices: https://apple.co/3d4eyZo
Download it here for Android Devices: https://bit.ly/2SrDulJ
Table of Contents
Dmitri Mendeleev - 0:45
Mendeleev's Organization of the Periodic Table - 2:31
Relationships in the Periodic Table - 5:03
Why Mendeleev Stood Out from his Colleagues - 7:09
How the Periodic Table Could be Improved - 8:28
More info about the cylindrical periodic table of elements: http://www.av8n.com/physics/periodic-table.htm
Crash Course is on Patreon! You can support us directly by signing up at http://www.patreon.com/crashcourse
Want to find Crash Course elsewhere on the internet?
Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse
Twitter - http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/thecrashcourse/
CC Kids: http://www.youtube.com/crashcoursekids
Whacky colour changes, magic disappearing water, blowing up dustbins, clouds of steam, thunder air explosions. Are you ready to fasten your seatbelts and enjoy the ‘explosive’ journey?
In his talk, Andrew aims to promote chemistry as the science of remarkable changes, which are often overlooked yet so important in our everyday life. And he does it brilliantly by performing an incredible series of 25 experiments in 15 minutes, totally amazing the audience (who rewards him with a long and deserved standing ovation)!
Andrew Z. Szydło is an internationally acclaimed chemistry teacher. But he’s definitely not the typical chemistry teacher you would expect…
He holds a PhD in the History and Philosophy of Science from UCL, and is an expert on the history of alchemy (his 1994 book ‘Water Which Does Not Wet Hands’ is considered to be the standard reference work on the Polish alchemist Michael Sendivogius.)
But his polymath spirit extends further: he’s a violin, bugle and accordion player, as well as a professional photographer. Throughout the years Andrew has wowed audiences all around the world with his pyrotechnical approach to teaching and demonstrating chemical sciences on stage and has appeared many times on TV. This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community. Learn more at https://www.ted.com/tedx
Follow us at https://www.facebook.com/AtomicSchool, https://www.instagram.com/AtomicSchools/ and https://twitter.com/atomicschools
Check out how the the Periodic Table is connected to Atomic Structure (protons, electrons and neutrons) at https://youtu.be/3_FJIpKgdV4.
Also check out how protons, electrons and neutrons were discovered at https://youtu.be/kBgIMRV895w.
Introduction video on the periodic table being explained to chemistry school & science students . The video explains how there are 92 naturally occurring elements, one for each kind of atom, and how they are arranged into a table according to their relative weights.
The expanded table is shown, and how this is abbreviated into the common Periodic Table. The division between metals, semi-metals and non-metals is discussed, with notable examples.
It also shows how the elements are arranged in rows and groups, the latter containing elements with similar properties, like members of a family.
Subscribe to watch more online chemistry courses & science videos:
http://www.youtube.com/channel..../UCiX8pAYWBppIbtUZTf
About Atomic School:
Atomic School supports the teaching of Atomic Theory to primary school & science students.
Our work has been verified by science education researchers at the University of Southern Queensland, Dr Jenny Donovan and Dr Carole Haeusler, who confirm that primary students are capable of learning much more complex scientific concepts than previously thought, and crucially, that they love it. Students run to class!
The program has been trialed in Australian schools as well as schools in the Philippines, Iran and India. It is conducted as holiday workshops at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation, the Queensland Museum as well as the World Science Festival.
It has attracted wide media interest, including TV, radio and print, and the research data has been presented at prestigious American Education Research Association and Australian Science Education Research Association conferences.
Atomic Theory underlies all the other sciences- genetics, electronics, nanotechnology, engineering and astronomy- so an early understanding will set them up for a more successful learning sequence for all their science subjects, and support their mastery of mathematics as well. We also have extension programs that cover Biology, Physics and Astronomy to an equal depth.
About Ian Stuart (Email: ian.douglas.stuart@gmail.com):
The founder of Atomic School, Ian Stuart, taught Chemistry and Physics for 25 years at senior levels before he realized that his 8-year old son, Tom, could understand Atomic Theory at a much deeper level than he expected.
Ian then developed a program to teach the advanced concepts of high school Chemistry, Physics and Biology to students 10 years younger than they normally would. He found that this engaged their interest in modern science early, and sustained it through to high school and beyond. It also sets them up for future success in their academic and career paths.
Ian has a Bachelor's Degree in Chemistry from the University of Queensland and a Master's degree in Electrochemistry from the University of Melbourne.
Connect with Atomic School on social media:
http://facebook.com/AtomicSchool
http://twitter.com/AtomicSchools
http://instagram.com/AtomicSchools
Video transcript:
In the first video we saw that all the things in the world are made of incredibly tiny particles called atoms. And also that there are 92 different kinds of them. Most things have more than one type of atom in them, but when we do find something containing just one kind of atom, we call it an element. A nugget of gold is an element because it's made of only gold atoms.
The atoms are too small to see with our eyes, even using a good microscope, but if we could zoom in with a magnification of a billion times we could see the individual gold atoms. Each kind of atom had a shorthand way of writing it, called its symbol, using either one or two letters. The symbol for gold is Au, taken from the ancient Latin word it, aurum. The symbol Au could refer to either a single gold atom, or the element gold consisting of many gold atoms.
Scientists have made a list of all the types of atoms, starting with the lightest, hydrogen, followed by the next lightest, helium. Just heavier than these are lithium and beryllium. We could give each element a number showing its place in this list. Hydrogen's number would be 1 as it is the first in the list, helium's would be 2, and so on. Here are the first 20 elements in the list, starting with the lightest, hydrogen, and going all the way to the heaviest, uranium. Since there are 92 elements in the list, uranium's number must be 92
More Lessons: http://www.MathAndScience.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/JasonGibsonMath
In this lesson, you will learn about the periodic table and how it is used in chemistry. We will focus on how the periodic table is organized by atomic number, and discuss how properties of elements are periodic in nature throughout the table due to the electrons in the outer shells of the atoms. We will also discuss atomic mass and valence electrons, including predicting when an atom will gain or lose an electron in a chemical reaction..
Provided to YouTube by Virgin Music Group
Chemistry 101 · 9th Wonder · Buckshot
Chemistry
℗ 2005 Duck Down Music Inc.
Released on: 2005-07-12
Writer: Kenyatta Blake
Writer: Patrick Douthit
Auto-generated by YouTube.
This video explains how the structure of the atom is directly responsible for the shape of the Periodic Table, and allows scientists to read the personality of each kind of atom due to its position. Protons, electrons, and neutrons explain everything about how an atom works and the making of the periodic table itself.
00:15 Scientists J J Thompson (1897), E Rutherford (1907) and J Chadwich (1932) discovery
00:25 Smaller particles: Positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons in the center called nucleus
00:51 The Nucleus
01:23 The atom is mainly empty space
01:46 Henry Moseley (1913) discovered that Atomic Number = Number of Protons
02:32 Number of protons = Number of electrons (in a neutral atom)
03:10 Isotopes
03:25 Atomic Mass Unit AMU
04:30 Neutorns have a big effect on the atomic weight but do not matter much in making chemical bonds
04:50 Electron Shells
05:15 Electrons are like guests in a hotel
06:20 Quantum Jump
06:38 Valence Electrons
07:00 Hydrogen
07:35 Helium
08:15 The Periodic Table
08:22 Lithium
08:52 Beryllium
09:00 Boron
09:17 Carbon
09:23 Nitrogen
09:30 Oxygen
09:35 Fluorine
09:39 Neon
09:55 Third shell
10:00 Sodium
10:30 Magnesium
10:40 Alkaline Earth Metals - the same number of valence electrons
11:53 Period 3
13:20 They can explain almost all of chemistry
13:38 Periodic Table Trends
14:00 Next video URL:
Video transcript:
“
To explain how atoms behave, we need to look inside them.
About a hundred years ago scientists discovered that atoms aren’t like tiny solid marbles as they thought, but made of three much, much smaller particles - positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons in their centre, called the nucleus, and negatively charged electrons orbiting on the outside in shells. See our video about how scientists discovered protons, electrons and neutrons at the link in the descrIption:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kBgIMRV895w
THE NUCLEUS
The nucleus is much smaller than shown here in the diagram. If an atom were the size of a football stadium, then its nucleus would be the size of a pea. This means the atom is mostly empty space. And so are YOU.
Even though the nucleus is tiny, it makes up over 99.9% of the atom’s mass. That’s because protons and neutrons are 2 thousand times heavier than electrons. So they don’t matter much.
In 1913, Henry Moseley discovered that an element’s Atomic Number was always the same as the number of protons in its nucleus. What a coincidence! This is now the modern definition of Atomic Number.
This atom has 5 protons so its Atomic Number is 5. This is the number above the element’s symbol on the PT. Which element is it? …. Boron.
In an electrically neutral atom, the number of positive Protons must equal the number of negative electrons so that their charges cancel. So a boron also has 5 electrons. The job of neutrons is to overcome the proton-proton repulsions, and to keep the nucleus together. Most boron atoms use 6 neutrons to stabilize their nuclei, but some can get away with 5. The number of neutrons can vary between atoms of the same kind, so scientists give these a special name- isotopes. So boron has two! isotopes.
Protons and neutrons both have a mass of about 1 atomic mass unit, or amu, or just u, or even the Dalton. They all mean the same thing, which is a bit annoying. Call me old fashioned, but I prefer amu. Scientists use this tiny mass unit for atoms as grams or pounds are too big. Electrons weigh hardly anything. So the atom’s mass is just the sum of its protons and neutrons. Both boron's have 5 protons, so its 6-neutron isotope would weigh 11, and its 5-neutron isotope 10 amu. It’s Atomic Weight shown on the PT is 10.8 and is the average of its two isotopes. It’s is closer to 11 because it’s the more abundant one.
Neutrons have a big effect on Atomic Weight, but don’t matter much in making chemical bonds, which we’re interested in here. So we’ll just look at protons and electrons from now on. Bye, bye neutrons. And Atomic Weights.
ELECTRON SHELLS
The first electron shell can accommodate 2 electrons before it’s full, while the 2nd shell can accommodate up to 8. This is why boron has only 2 electrons in its 1st shell, and the remaining 3 electrons in the 2nd shell.
Electrons are like guests in a hotel. Here’s a normal hotel. And here’s the Quantum Hotel that better shows how electrons fit around an atom. The 1st floor can take 2 guests before it’s full, the 2nd floor also 8, the 3rd floor 8, and the 4th and 5th 18 each. When a floor is full a new arrival is sent to the next floor up. This guest on the 4th floor has more energy than the guests below, which she would find out if she jumped. When she lands, the energy she had turns into sound energy. Electrons in higher levels also have more energy, and when they jump down, light energy is emitted instead. This is called a quantum jump.
“
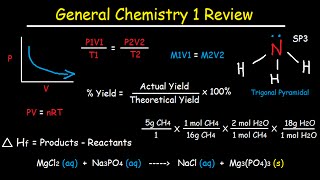
This video tutorial study guide review is for students who are taking their first semester of college general chemistry, IB, or AP Chemistry. Even if you’re studying for the general chemistry section of the MCAT, DAT, PCAT, OAT or SAT Subject chemistry test, this video can help give you a nice overview of all the topics you need to learn in General Chemistry 1. This introduction video contains plenty of examples and practice problems to help prepare you for the final exam. It has about 160 multiple choice questions in the form of a practice test. Feel free to use it as a study guide. The solutions to each problem is provided as well as the equations and formulas that you need to solve it.
Full 8 Hour Video on Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/MathScienceTutor
Direct Link to The Full Video:
https://bit.ly/3GstGjy
Download Exam - 160 Problems:
https://bit.ly/3VTpcbj
Chemistry PDF Worksheets:
https://www.video-tutor.net/ch....emistry-basic-introd
___________________________________
Full 8 Hour Video on YouTube:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gdibXTHoKCg
Join The Membership Program:
https://bit.ly/46xaQTR
This is for those who are struggling to figure out how to self-study A Level H2 Chemistry. #singapore #alevels #chemistry
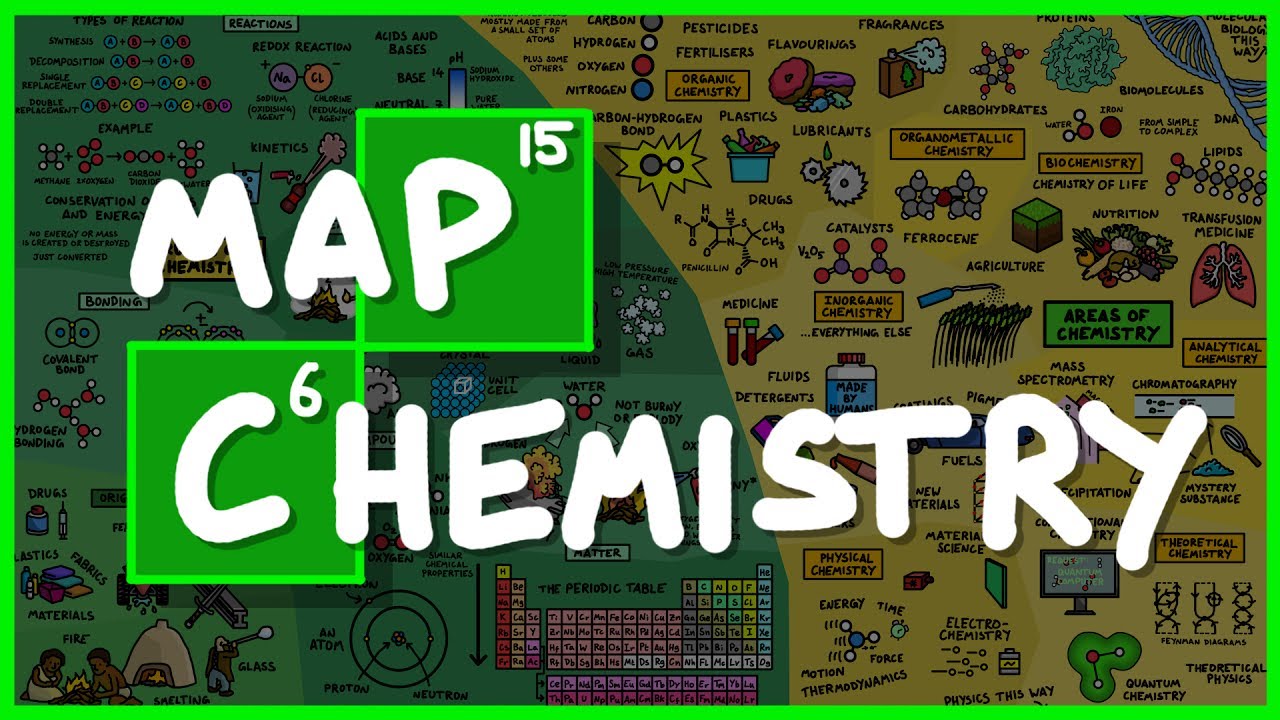
The entire field of chemistry summarised in 12mins from simple atoms to the molecules that keep you alive.
#chemistry #DomainOfScience
If you would like to buy a poster of this map, they are available here: https://www.redbubble.com/peop....le/dominicwalliman/w
I have also made a version available for educational use which you can find here: https://flic.kr/p/UBS4mf
and a widescreen version: https://flic.kr/p/UNA1LW
Errata and notes:
1. I got the Oxidising Agent and the Reducing Agent the wrong way around! Sodium is the Reducing agent and Chlorine is the Oxidising agent. My confusion was that when a sodium atom looses an electron it becomes oxidised, so in my simple brain, I called it the oxidising agent. That is wrong because the agent that oxidises the sodium is the chlorine atom and so the labels are the wrong way around. Doh!
2. I drew the hydrogen H2 molecule with a double bond but it should be a single bond because they are bonded with a single covalent bond.
3. Where I have drawn carbon dioxide, the carbon should have a double bond to each of the oxygens.
4. Apparently Feynman diagrams are not that useful for theoretical chemistry, so perhaps that wasn't the best choice for the illustration. The feedback in the comments from a real theoretical chemist is "All we deal with is shuffling around electrons, but many many many electrons, so a Feynman diagram would need to be huge but at the same time would be very very repetitive."
5. In analytical chemistry, I should have called it distillation rather than precipitation.
6. My definition of organic chemistry being about ‘life’ is not very good. I should have said that organic chemistry looks at compounds that contain carbon. But there are some compounds in inorganic chemistry that also contain carbon, like carbon dioxide so I guess I'd also have to state that inorganic chemistry is almost everything else.
7. I said that fuels are inorganic chemistry which is misleading when I drew a car next to it. My understanding is that there are inorganic fuels that don't contain carbon, but obviously all the fuels we are familiar with are organic. I thought a picture of a car would tie a few things together elegantly, but it ended up giving the wrong impression. That’s okay, I’m still learning! :D
8. In inorganic chemistry, I should have stated that all natural minerals fall under inorganic chemistry so as not to be misleading, otherwise you might go way thinking that only man-made substances fall under inorganic chemistry which is not true. I said that 'a lot of the inorganic compounds that are studied are man-made' meaning that the cutting edge of research is mostly man-made substances.
9. Apparently water is not the most inflammable substance. I thought it was so that is interesting.
10. In the bonding section, hydrogen bonding and van der waals forces are technically inter molecular forces.
Here are some of the references I used for this video if you’d like to dig a little deeper
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemistry
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Outline_of_chemistry
https://www.uwlax.edu/chemistr....y-and-biochemistry/s
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/chemistry
https://www.cancerquest.org/ca....ncer-biology/biologi
Early smelting:
http://ispatguru.com/evolution....-of-blast-furnace-ir
Categorisation of reactions
http://www2.ucdsb.on.ca/tiss/s....tretton/chem1/stoich
Thanks so much to my supporters on Patreon. If you enjoy my videos and would like to help me make more this is the best way and I appreciate it very much. https://www.patreon.com/domainofscience
Frontiers of Space: http://nobrow.net/shop/profess....or-astro-cats-fronti
Atomic Adventure: http://nobrow.net/shop/profess....or-astro-cats-atomic
Intergalactic Activity Book: http://nobrow.net/shop/profess....or-astro-cats-interg
Solar System App: http://www.minilabstudios.com/....apps/professor-astro
Find me on twitter, instagram, and my website:
http://dominicwalliman.com
https://twitter.com/DominicWalliman
https://www.instagram.com/dominicwalliman
https://www.facebook.com/dominicwalliman
In this video we read about :----
introduction
sources of water
impurities in water
sources of impurities in water
and specification of water for different uses
Chemistry for General Biology students. This video covers the nature of matter, elements, atomic structure and what those sneaky electrons do. AND as a bonus, I cover Lewis dot diagrams -- which most of you won't see in your general biology class -- but they will help you SO MUCH you'll wonder how you've lived without them!
#chemistry #atoms #nursingstudent #biologystudent #chemistrybasics #chemistrystudent
Part II is here: http://youtu.be/Juw7HBg0zZs
Penguin Prof Staff:
Organic chemistry consultant in residence: FabioChem (Fabio Agnelli, Ph.D)
Happiness Coordinator: Flops the Penguin
Content Creator, Producer, Editor and Narrator: The Penguin Prof (Valerie Pennington)
Let's Connect!
https://hihello.me/hi/penguinprof-U55i9g
Want more Penguin Prof?
Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/user/ThePenguinProf
FB Page: https://www.facebook.com/ThePenguinProf
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/penguinprof/
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@penguinprof
Twitter: https://twitter.com/penguinprof
Web: http://www.penguinprof.com/
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/penguinprof
Videos You Might Like:
Monomers vs. Polymers: https://youtu.be/kuXffvNVjhM
Your Blood Sugar (Insulin vs. Glucagon): https://youtu.be/G2wdkoOZiAQ
Levels the Protein Structure: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OwkKw53dBtQ
Redox Relief: http://youtu.be/eL0BH5O9Sdo
Understanding Chemical Structures: http://youtu.be/FbaXQ8u6IP8
How Hormones Work: http://youtu.be/KnIu7DDflw8
Enzyme Regulation Explained: https://youtu.be/b2Ebt2nU6iM
Blood Types: ABO and Rh: http://youtu.be/L06TJTMVkBo
Cell Membranes EXPLAINED: https://youtu.be/ErPyWp3THbU
Chemistry Basics: Osmolarity, Osmolality and Tonicity: https://youtu.be/LeRw4Be5SnU
Making Happy: Serotonin, Antidepressants and Psychedelics: https://youtu.be/2fQYBTO0qAM
Equilibrium Potentials and Driving Force: https://youtu.be/Kdnj0o1Wxqg
Take Great Notes: https://youtu.be/pYRmNql_12s
Should You Use Your Textbook? https://youtu.be/9m50QeXtpBM
Homeostasis and Feedback: https://youtu.be/mn-2ob0F5e8
Epidemiology Basics - Reproductive Number R0: https://youtu.be/om5aLPdwTyc
Cardiac Pressure / Volume Curves: https://youtu.be/8FpV6qxmiJ4
All Rights Reserved © 2024, The Penguin Prof
Penguin Prof is Supported BY AUDIBLE.COM
PenguinProf LOVES Audible and now the feeling is mutual! Audible.com is the premier provider of digital audiobooks. Audible has over 150,000 titles to choose from in every genre. Audible titles play on iPhone, Kindle, Android and more than 500 devices for listening anytime, anywhere. Click to learn more and download a FREE audiobook of your choice! http://www.audibletrial.com/PenguinProf
This video tutorial provides a basic introduction into chemistry. You can access the full video at the link shown below:
Full Video on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/MathScienceTutor
Direct Link to The Full Video:
https://bit.ly/3hIRJCx
___________________________
Full 1 Hour 42 Minute Video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oK3XF1gdPGM
Join The Membership Program:
https://bit.ly/46xaQTR
Here is a list of topics:
1. Intro to the Periodic Table of the Elements
2. Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals, Transition Metals, Chalcogens, Halogens, and Noble Gases
3. Ion Charges of Representative Elements
4. Atoms, Molecules, Pure Elements, and Compounds
5. Ionic Compounds and Molecular Compounds
6. Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
7. Atoms vs Ions
8. Cations and Anions
9. Nomenclature of Molecular Compounds
10. How To Name Ionic Compounds
11. Naming Ionic Compounds With Transition Metals & Roman Numerals
12. Polyatomic Ions
13. Writing Chemical Formulas of Ionic Compounds
14. Average Atomic Mass
15. Isotopes
16. How To Determine The Number of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons In Atoms and Ions
Hank does his best to convince us that chemistry is not torture, but is instead the amazing and beautiful science of stuff. Chemistry can tell us how three tiny particles - the proton, neutron, and electron - come together in trillions of combinations to form ... everything. In this inaugural episode of Crash Course Chemistry, we start out with one of the biggest ideas in chemistry ever - stuff is made from atoms. More specifically, we learn about the properties of the nucleus and why they are important to defining what an atom actually is.
This video is available in Spanish on our Crash Course en Español channel! Watch it here: https://youtu.be/G7wUMpsB5k8
Pssst... we made flashcards to help you review the content in this episode! Find them on the free Crash Course App!
Download it here for Apple Devices: https://apple.co/3d4eyZo
Download it here for Android Devices: https://bit.ly/2SrDulJ
Table of Contents
Intro 00:00
Einstein & Atoms 02:05
Composition of Atoms 03:18
Atomic Number 04:20
Isotopes 08:04
Relative Atomic Mass 07:26
Mass Number 07:44
Watch the SciShow episodes on the Strong Nuclear Force here:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yv3EMq2Dgq8
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BNDOSMqGLlg
Crash Course is on Patreon! You can support us directly by signing up at http://www.patreon.com/crashcourse
Want to find Crash Course elsewhere on the internet?
Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse
Twitter - http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/thecrashcourse/
CC Kids: http://www.youtube.com/crashcoursekids
More Lessons: http://www.MathAndScience.com
Twitter: https://twitter.com/JasonGibsonMath
In this lesson, you will learn what the study of chemistry entails, why chemistry is important, and the basic ideas studied in any introduction to chemistry. We describe chemistry as the study of matter and the chemical rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction. In chemistry, reactants are mixed together and products are formed. The products are formed as a result of the atoms in the reactants transferring or sharing electrons, and rearranging the order of the atoms and how the atoms are bonded. Chemical bonds are broken in the reactants, and bonds are formed in the products. In chemistry, we want to understand how these reactions occur, and we learn how to calculate how much product will form. We are also interested in how these reactions occur in aqueous (water) solution, as this is central in many chemical reactions. We also study the electron configuration of the atoms, gas laws including the ideal gas law, chemical kinetics, equilibrium, and more..
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/chemistry/atom
A big picture view of chemistry and why it is fascinating. How chemistry relates to math and other sciences.
View more lessons or practice this subject at https://www.khanacademy.org/sc....ience/chemistry/atom?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc&utm_campaign=chemistry
Khan Academy is a nonprofit organization with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. We offer quizzes, questions, instructional videos, and articles on a range of academic subjects, including math, biology, chemistry, physics, history, economics, finance, grammar, preschool learning, and more. We provide teachers with tools and data so they can help their students develop the skills, habits, and mindsets for success in school and beyond. Khan Academy has been translated into dozens of languages, and 15 million people around the globe learn on Khan Academy every month. As a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization, we would love your help! Donate or volunteer today!
Donate here: https://www.khanacademy.org/donate?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
Volunteer here: https://www.khanacademy.org/contribute?utm_source=youtube&utm_medium=desc
This online chemistry video tutorial provides a basic overview / introduction of common concepts taught in high school regular, honors, and ap chemistry as well as college general chemistry.
Significant Figures Review: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l2yuDvwYq5g
Unit Conversion Problems:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eK8gXP3pImU
Accuracy and Precision:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0IiHPKAvo7g
Density Practice Problems:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9CKDQE35qXQ
_________________________________
Physical and Chemical Changes:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YE2xaMsoGFU
Physical Vs Chemical Properties:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gH1R87ahFvA
Protons, Neutrons, & Electrons:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=65dDZulPhtg
Average Atomic Mass:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JT18bDAadQ0
Ionic and Covalent Bonding:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uDFLHTDJ4XA
______________________________________
Naming Molecular Compounds:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3agUL7-ezXk
Naming Ionic Compounds:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5rSgduXqhhU
Naming Acids In Chemistry:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r7PfTMAFYgs
Stoichiometry Problems:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mP2Yg8alyR0
Solution Stoichiometry :
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ab3wfKjaWWQ
Final Exams and Video Playlists:
https://www.video-tutor.net/
This is just a few minutes of a complete course.
Get full lessons & more subjects at: http://www.MathTutorDVD.com.
In this lesson the student will be introduced to the core concepts of chemistry 1..







![The Periodic Table of the Elements in Chemistry - [1-2-12]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/CTwua04Ykso/maxresdefault.jpg)







![Intro to Chemistry & What is Chemistry? - [1-1-1]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pdyDmXtye2w/maxresdefault.jpg)



